|
AUTONOMOUS NAVIGATION
ABOUT - CIRCUMNAVIGATION - CONTACTS - FOUNDATION - HOME - A-Z INDEX
ROBOTIC OCEAN CONDITIONER - This vessel is designed to operate in unmanned fleets to target ocean waste before it settles on the ocean floor where nobody can recover it. There is nothing like it in existence today, though other ideas for trapping plastic waste are being developed, such as that of Boyan Slat. Autonomy in terms of energy harvesting and ocean navigation are essential elements of the SeaVax system.
One of the key technologies in any ocean cleaning operation is the cost effective operation of SeaVax machines. This involves the development and testing of an operating system that is capable of navigating without human intervention to COLREGs standards, save only that there are human eyes on board at all times remotely monitored via a shore based operations headquarters.
Autonomous Unmanned Navigation has been a military objective for some years ending with the launch of the American warship funded by DARPA. On land the military have been active in this area of research with ......
These technologies are used to develop machines that can substitute for humans. Robots can be used in any situation and for any purpose, but today many are used in dangerous environments (including bomb detection and de-activation), manufacturing processes, or where humans cannot survive. Robots can take on any form but some are made to resemble humans in appearance. This is said to help in the acceptance of a robot in certain replicative behaviors usually performed by people. Such robots attempt to replicate walking, lifting, speech, cognition, and basically anything a human can do. Many of today's robots are inspired by nature, contributing to the field of bio-inspired robotics known as animatronics.
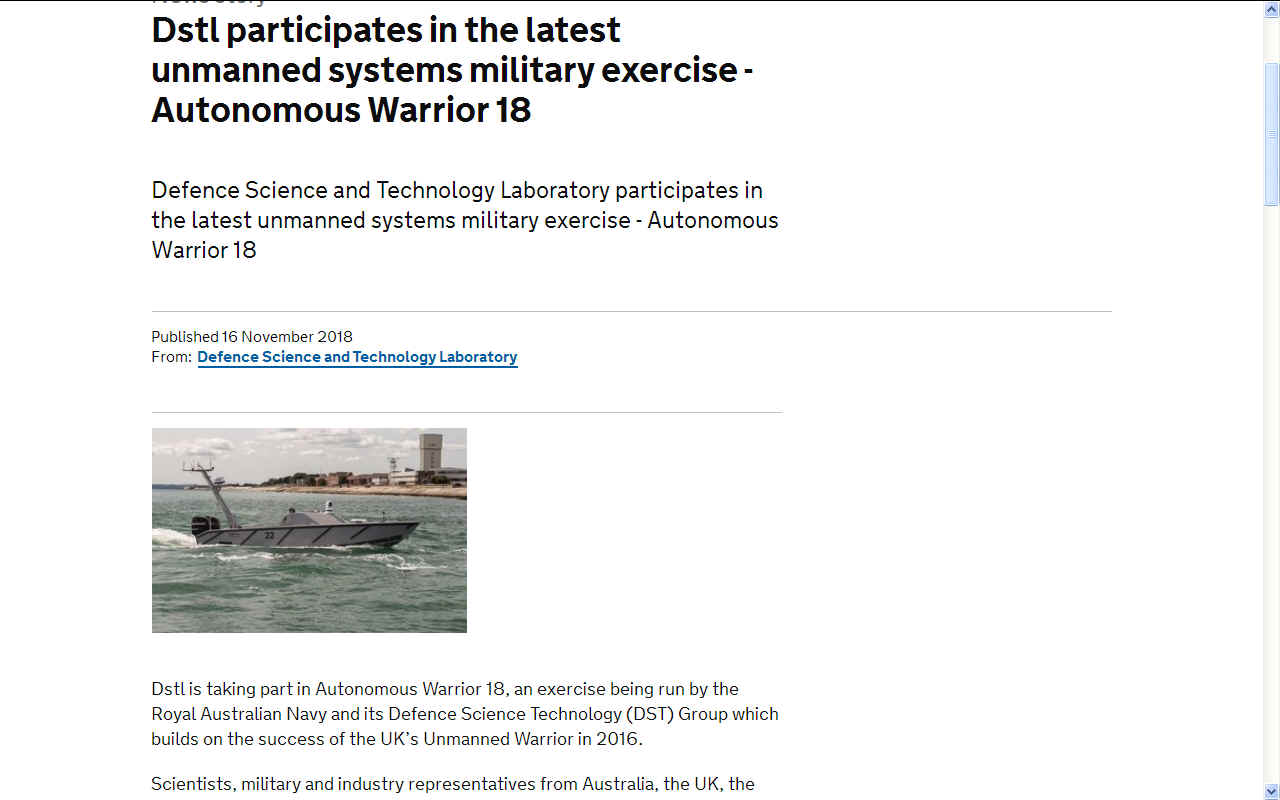
DSTL
- is taking part in Autonomous Warrior 18, an exercise being run by the Royal Australian Navy and its Defence Science Technology (DST) Group which builds on the success of the UK’s Unmanned Warrior in 2016.
XU Tao: PhD 2004-2007
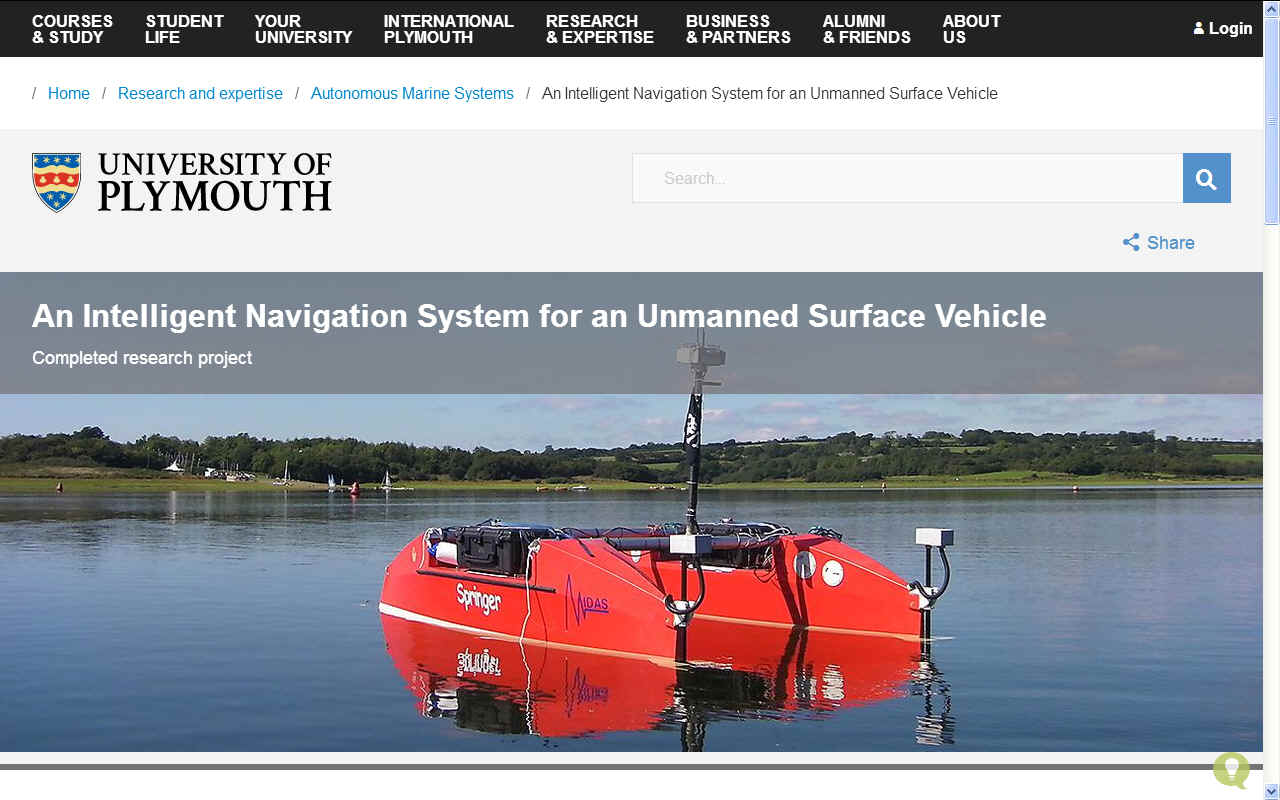
- A multi-disciplinary research project has been carried out at the
University of Plymouth to design and develop an Unmanned Surface Vehicle (USV) named Springer. The work presented herein relates to formulation of a robust, reliable, accurate and adaptable navigation system to enable Springer to undertake various environmental monitoring tasks. Synergistically, sensor mathematical modelling, fuzzy logic, Multi-Sensor Data Fusion (MSDF), Multi-Model Adaptive Estimation (MMAE), fault adaptive data acquisition and an user interface system are combined to enhance the robustness and fault tolerance of the on board navigation system. This thesis not only provides a holistic framework but also a concourse of computational techniques in the design of a fault tolerant navigation system. One of the principle novelties of this research is the use of various fuzzy logic based MSDF algorithms to provide an adaptive heading angle under various fault situations for Springer.
Reynolds Building Drake Circus, Plymouth PL4 8AA, United Kingdom
DARPA’s Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) Continuous Trail Unmanned Vessel (ACTUV) program - now known as Sea Hunter, or the Medium Displacement Unmanned Surface Vessel (MDUSV) - is an unmanned surface vessel to detect and track diesel-electric submarines. The program's lead contractor is Leidos (formerly SAIC) which used an autonomous surrogate vessel called Pathfinder to develop the ACTUV's technology.
ROBOT CONFERENCE - Collaborative Robots and Advanced Vision are two of the most cutting-edge topics in automation today. At this two day conference you will explore a range of current advancements in both fields focusing on technology, applications, safety implications, and human impacts. Whether you're looking to implement your first ever automation system, take your current system past its limitations, grow your understanding of the available technology, or learn more about the market in general, this conference is right for you!
The concept of creating machines that can operate autonomously dates back to classical times, but research into the functionality and potential uses of robots did not grow substantially until the 20th century. Throughout history, it has been frequently assumed that robots will one day be able to mimic human behavior and manage tasks in a human-like fashion. Today, robotics is a rapidly growing field, as technological advances continue; researching, designing, and building new robots serve various practical purposes, whether domestically, commercially, or militarily. Many robots are built to do jobs that are hazardous to people such as defusing bombs, finding survivors in unstable ruins, and exploring mines and shipwrecks and disposing of nuclear waste. Robotics is also used in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) as a teaching aid.
LINKS & REFERENCE
http://www.navaldrones.com/ACTUV.html https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autonomous_underwater_vehicle http://www.unmanned-ship.org/munin/about/the-autonomus-ship/ https://www.plymouth.ac.uk/research/autonomous-marine-systems/springer-1-unmanned-surface-vehicle https://www.plymouth.ac.uk/research/autonomous-marine-systems/springer-2 https://www.plymouth.ac.uk/research/autonomous-marine-systems/an-intelligent-navigation-system-for-an-unmanned-surface-vehicle https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autonomous_Navigation_System https://www.a3automate.org/ https://www.robotics.org/
This website is provided on a free basis as a public information service. Copyright © Cleaner Oceans Foundation Ltd (COFL) (Company No: 4674774) 2021. Solar Studios, BN271RF, United Kingdom. COFL is a charity without share capital. The names Amphimax™ RiverVax™ and SeaVax™ are trademarks.
|