|
SOLAR ARRAYS
ABOUT - CIRCUMNAVIGATION - CONTACTS - CROWDFUNDING - DONATE - FOUNDATION - HOME - A-Z INDEX
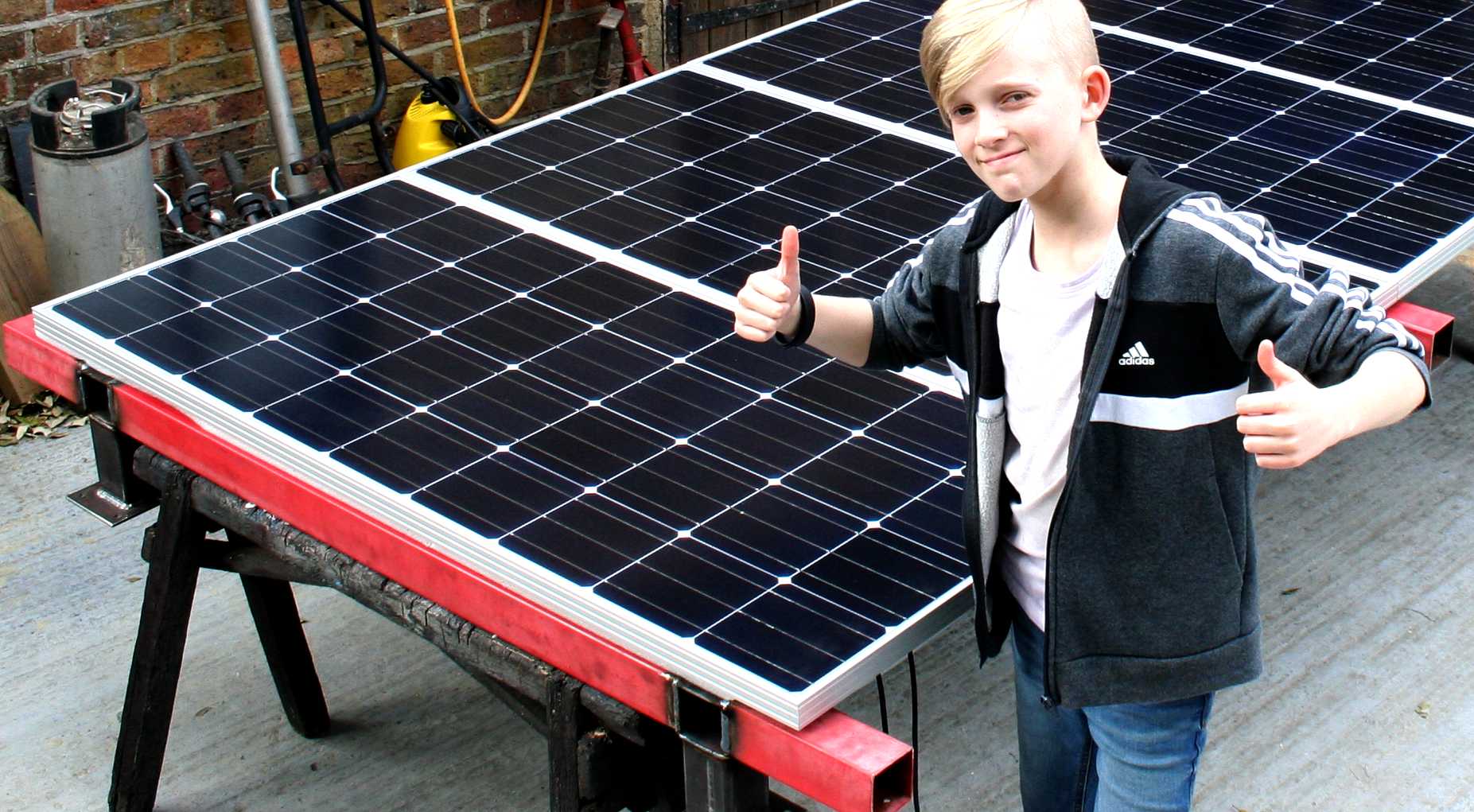
SOLAR PANELS - Ryan helped to make sure that these solar panels will fit within the width of a steel frame to be fixed to a Ford Transit roof, so that there would be sufficient clearance for overlapping arrays. This experimental rig will track the sun and move arrays on either side of these fixed panels to increase the harvestable light energy. Copyright photograph © 22-04-19 Cleaner Ocean Foundation Ltd, all rights reserved.
FOLDED STACK - The picture above shows the hinge post and shell bearings for the shafts that turn the solar panel arrays as an end view. The shafts are driven by a hydraulic motor that is either directly coupled or chain driven to multiply the torque and/or slow the movement, as may be desired for controllability. See the plan view diagram below. Copyright diagram © 27-04-19 Cleaner Ocean Foundation Ltd, all rights reserved.
ARRAY BEARINGS - The mountings for the solar panels arrays of a Ford Transit based mobile test rig, consist of four plain steel bearings on each side of a hefty steel frame in hinge fashion for simplicity. The bearings on one side of the frame are higher than the other to allow the panels to fold over the fixed central bank for ultimate protection at sea, in storm conditions. Alignment is crucial to reduce the turning torque for the hydraulic motors. Copyright photograph © 26-04-19 Cleaner Ocean Foundation Ltd, all rights reserved.
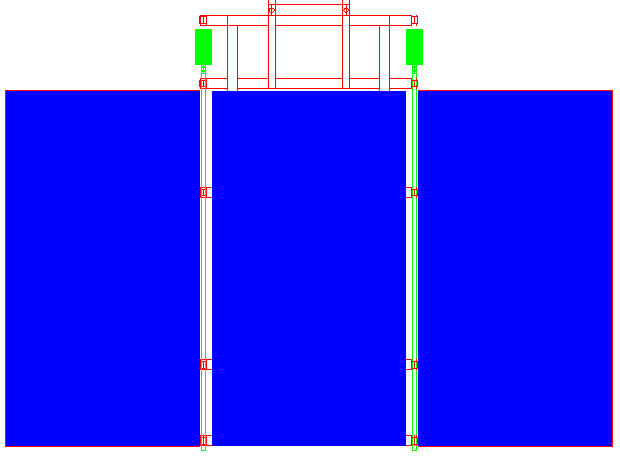
ARRAY PLAN VIEW - This diagram shows the solar array folded open looking from above such that they present flat on to the sun. The hydraulic motors and hinge shafts are shown in green. This experimental rig provides 1.8kW of power in total. The SeaVax needs around 220 square meters of panels of which some 124m2 are moving arrays that track the sun. Each moving array on SeaVax would carry 62m2 of panels compared to the 3.8m2 of these arrays. Copyright diagram © 29-04-19 Cleaner Ocean Foundation Ltd, all rights reserved.
In the 1950s solar cells were developed by the US (Bell Labs for NASA) and Russia as part of their search for ways of powering satellites and space craft. In 1967 Soyuz 1 was the first manned space craft to be powered by solar cells.
Terrestrial take up was slow due to the expense and low efficiency of early commercially available cells. Oil companies such as BP helped to develop solar panels with greater efficiency, but today most of the development and manufacturing of solar technology is in China.
EXTINCTION OF SPECIES - From blue planet to scorched earth because vested interests prevented politicians from putting the brakes on. Economics stopped them thinking about the safety of life on earth. They'd rather die richer, than live, gambling with the future of our children and every other species on earth.
THE SOLAR DEVELOPMENT TIMELINE IS SOMETHING LIKE THIS:
1800s
1839 - Alexandre Edmond Becquerel observes the photovoltaic effect via an electrode in a conductive solution exposed to light.
1873 - Willoughby Smith finds that selenium shows photoconductivity.
1877 - W.G. Adams and R.E. Day observed the photovoltaic effect in solidified selenium, and published a paper on the selenium cell. 'The action of light on selenium,' in "Proceedings of the Royal Society, A25, 113.
1878 - Augustin Mouchot displays a solar power generator at the Universal Exhibition in Paris.
1883 - Charles Fritts develops a solar cell using selenium on a thin layer of gold to form a device giving less than 1% efficiency.
1900–1929
1901 - Philipp von Lenard observes the variation in electron energy with light frequency.
1930–1959
1932 - Audobert and Stora discover the photovoltaic effect in Cadmium selenide (CdSe), a photovoltaic material still used today.
1935 - Anthony H. Lamb receives patent US2000642, "Photoelectric device."
1941 - Russell Ohl files patent US2402662, "Light sensitive device."
1953 - Gerald Pearson begins research into lithium-silicon photovoltaic cells.
1954 - On April 25, 1954, Bell Labs announces the invention of the first practical silicon solar cell. Shortly afterwards, they are shown at the National Academy of Science Meeting. These cells have about 6% efficiency. The New York Times forecasts that solar cells will eventually lead to a source of "limitless energy of the sun."
1955 - Western Electric licences commercial solar cell technologies. Hoffman Electronics-Semiconductor Division creates a 2% efficient commercial solar cell for $25/cell or $1,785/watt.
1957 - AT&T assignors (Gerald L. Pearson, Daryl M. Chapin, and Calvin S. Fuller) receive patent US2780765, "Solar Energy Converting Apparatus." They refer to it as the "solar battery." Hoffman Electronics creates an 8% efficient solar cell.
1958 - T. Mandelkorn, U.S. Signal Corps Laboratories, creates n-on-p silicon solar cells, which are more resistant to radiation damage and are better suited for space. Hoffman Electronics creates 9% efficient solar cells. Vanguard I, the first solar powered satellite, was launched with a 0.1W, 100 cm² solar panel.
1959 - Hoffman Electronics creates a 10% efficient commercial solar cell, and introduces the use of a grid contact, reducing the cell's resistance.
1960–1979
1960 - Hoffman Electronics creates a 14% efficient solar cell.
1980–1999
1980 - John Perlin and Ken Butti's landmark book A Golden Thread published, covering 2500 Years of Solar Technology from the Greeks and Romans until the modern day.
1980 - The Institute of Energy Conversion at University of Delaware develops the first thin film solar cell exceeding 10% efficiency using Cu2S/CdS technology.
1991 - President George H. W. Bush directs the U.S. Department of Energy to establish the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (transferring the existing Solar Energy Research Institute).
1991 - Polegate, Sussex: a British inventor calculates from charts that there is sufficient solar energy to power a boat around the world. He proposes and names his course the "Sunshine Route."
1992 - The PV Pioneer Program started at Sacramento Municipal Utility District (SMUD). It was the first broad based commercialization of distributed, grid-connected PV system ("roof-top solar").
1993
- In England the SolarNavigator, the first solar boat designed
to attempt a circumnavigation of the globe becomes a small
scale model.
1994-5
The SolarNavigator is displayed at the Earls Court boat show
as a 1/20th scale model.
2000–2018
2003 -
George Bush has a 9 kW PV system and a solar thermal systems installed on grounds keeping building at the White House
2004 - Kansas Governor Kathleen Sebelius issued a mandate for 1,000 MWp renewable electricity in Kansas by 2015 per Executive Order 04-05.
2007 - The Vatican announced that in order to conserve Earth's resources they would be installing solar panels on some buildings, in "a comprehensive energy project that will pay for itself in a few years."[16]
2011 - Fast-growing factories in China push manufacturing costs down to about $1.25 per watt for silicon photovoltaic modules. Installations double worldwide.
2012 - A large boat called PlanetSolar circumnavigates the globe using solar power.
2013 - After three years, the solar panels ordered by President Barack Obama were installed on the White House.
2016 - University of New South Wales engineers established a new world record for unfocused sunlight conversion to electricity with an efficiency increase to 34.5%. The record was set by UNSW’s Australian Centre for Advanced Photovoltaics (ACAP) using a 28 cm² four-junction mini-module – embedded in a prism – that extracts the maximum energy from sunlight. It does this by splitting the incoming rays into four bands, using a four-junction receiver to squeeze even more electricity from each beam of sunlight.
2016 - First Solar says it has converted 22.1 percent of the energy in sunlight into electricity using experimental cells made from cadmium telluride - a technology that today represents around 5 percent of the worldwide solar power market.
2018 - Alta Devices, a US-based specialty gallium arsenide (GaAs) PV manufacturer, claimed to have achieved a solar cell conversion efficiency record of 29.1%, as certified by Germany's Fraunhofer ISE CalLab.
2019 - Cleaner Ocean Foundation begins construction of a portable solar generator.
LINKS & REFERENCE
https:
ROBOTIC OCEAN CONDITIONER - This solar and wind powered vessel is designed to operate in fleets to target ocean waste before it settles on the ocean floor where nobody can recover it. There is nothing like it in existence today, though other ideas for trapping plastic waste are being developed, such as that of Boyan Slat and the Seabin.
This website is provided on a free basis as a public information service. Copyright © Cleaner Oceans Foundation Ltd (COFL) (Company No: 4674774) 2019. Solar Studios, BN271RF, United Kingdom. COFL is a charity without share capital. The names Amphimax™ RiverVax™ and SeaVax™ are trademarks.
|